Are you grappling with the intricacies of cloud networking and the associated costs? Understanding the nuances of Amazon Web Services (AWS) NAT Gateways, from their functionality to their pricing structure, is crucial for optimizing your cloud infrastructure and avoiding unexpected expenses.
The digital landscape has undergone a seismic shift, with businesses of all sizes migrating their operations to the cloud. Within the AWS ecosystem, NAT Gateways play a vital role in enabling instances within a private subnet to connect to the internet or other AWS services while shielding their private IP addresses. This crucial function, however, comes with a cost, and a thorough understanding of this cost is paramount for effective cloud management.
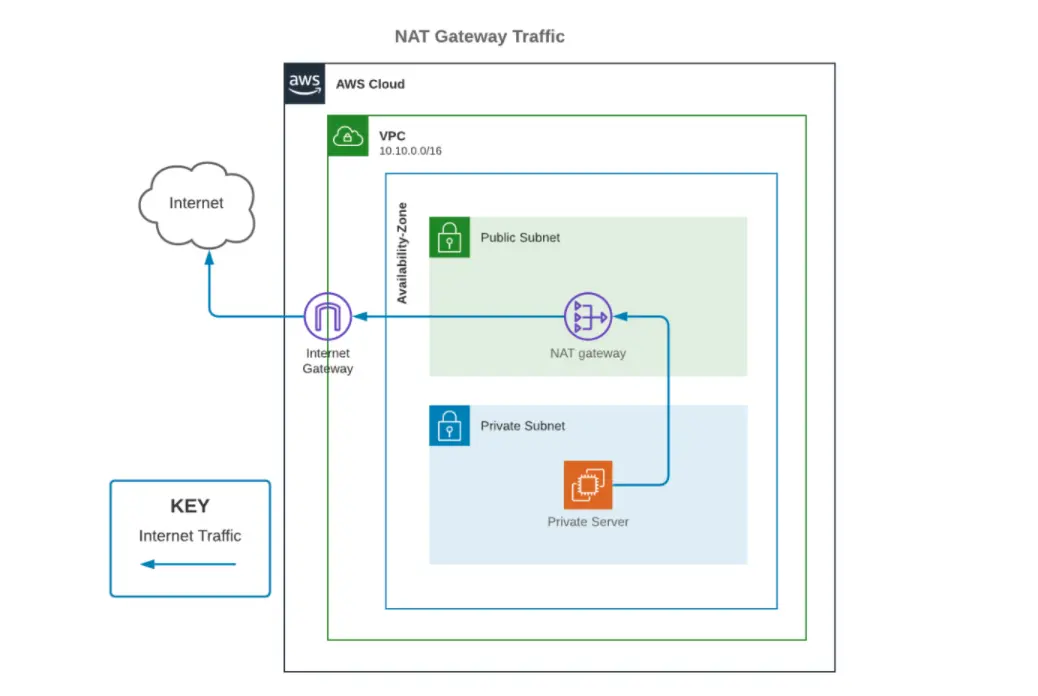
Consider a scenario: you've established a private subnet within your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and deployed an EC2 instance. This instance requires internet access, perhaps to download updates, access external APIs, or connect to other services. The NAT Gateway serves as the intermediary, allowing this communication to occur securely and efficiently. However, the provision of this service incurs charges based on two primary factors: the hourly availability of the NAT Gateway and the volume of data it processes.
AWS clearly outlines the pricing model, providing a straightforward approach that measures volume and frequency of use. When you provision a NAT Gateway, you are charged for each hour that it is available and for each gigabyte of data that it processes. This simplicity, however, belies the potential for significant costs, especially in environments with high traffic volume. It's a model that necessitates careful monitoring and optimization to avoid unnecessary expenditure.
The cost-effectiveness of the NAT Gateway, in comparison to other AWS services, hinges heavily on your specific use case and the volume of data flowing through it. While the AWS NAT Gateway provides a managed solution, the pricing structure demands that cloud architects and administrators diligently monitor network traffic, considering alternatives where appropriate. For detailed insights into potential cost savings, refer to AWS PrivateLink pricing, a service that can help you reduce data transfer charges.
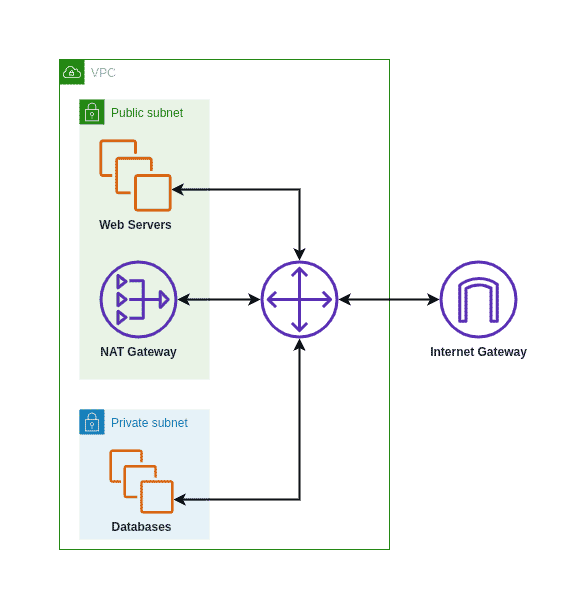
Let us delve deeper into the specifics. The fundamental operational principle of a NAT Gateway is to map the source private IPv4 address of your instances to the private IPv4 address of the NAT Gateway. This action effectively hides the internal IP addresses of your instances from the external world, a significant security advantage. This is true for both private and public NAT Gateways. However, in the case of a public NAT Gateway, the communication is directed through the internet gateway, ensuring a public facing route for the NAT'ed traffic.
The costs associated with using a NAT Gateway can be segmented into the following: the hourly charge and the data processing cost. The hourly charge is levied for the time the NAT Gateway is running, while the data processing cost is computed based on the volume of data transferred. It is worth noting that the pricing begins at $0.045 per NAT Gateway hour, with additional charges for data processing and data transfer. Moreover, data transfer costs are the customary costs incurred to move data between an EC2 instance and the internet.
However, the pricing does not stop there. If the bulk of traffic routed through your NAT Gateway flows towards AWS services, the charges for other AWS solutions such as Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) still apply. This includes the data transfer charges as per the published rates for these resources. Its imperative to consider all these factors while designing your AWS infrastructure.
Consider this: you've set up a NAT Gateway and configured your EC2 instance to route internet traffic through it. While this configuration provides the functionality you need, understanding and managing the associated costs becomes critical. The initial setup involves the hourly charge. Subsequently, as your instances communicate with the internet, the data processing charges begin accumulating. These costs can quickly escalate if not carefully monitored and optimized.
The choice of whether to use a NAT Instance or a NAT Gateway, or indeed any other architecture, demands careful consideration. As an illustration, both NAT Gateways and AWS Transit Gateways are utilized to manage network traffic within AWS environments. However, they serve distinct purposes and are adapted to different scenarios. A detailed comparison could help you select the most appropriate architecture for your specific requirements.
AWS does not offer reserved instances or spot pricing for NAT Gateways. Therefore, there is no means to curtail the expenses of operating a NAT Gateway. Unlike EC2 instances, AWS does not give reserved instances or spot pricing options on NAT Gateways. Hence, there is no way to reduce the overall cost. This necessitates diligent planning and optimization to mitigate cost overruns.
To make informed decisions, you must explore the available options, and understand the cost implications of each. The AWS Pricing Calculator, coupled with the judicious use of maintenance windows, offers valuable resources to help you optimize your costs. These tools empower you to forecast your expenditure and tailor your configuration for enhanced efficiency. Compare the prices, performance, and features of different NAT devices and examine examples of use cases to determine the best fit for your business needs.
The question of whether there's a difference in pricing when using a single Elastic IP versus multiple Elastic IPs with a NAT Gateway remains. It's a subtle yet important consideration that can impact overall costs. Understanding this nuance can allow you to further refine your configurations for maximum cost efficiency.
Furthermore, understanding the pricing of different NAT devices will help you determine whether to opt for the NAT instance or the NAT Gateway for your VPC. This includes comparing the prices, performance, and features. Careful consideration of these factors will empower you to choose a cost-effective and high-performing solution.
In essence, managing the costs associated with AWS NAT Gateways necessitates a proactive, informed, and strategic approach. By grasping the pricing model, scrutinizing your traffic patterns, and leveraging available tools, you can optimize your cloud infrastructure, control expenses, and ensure that your cloud journey is as cost-effective as it is efficient.