Are you ready for tax season in the Peach State? Navigating the complexities of Georgia's income tax system is crucial for every resident, and understanding the deadlines, rates, and available resources is key to a smooth filing experience.
As the calendar turns and the financial year draws to a close, Georgians are once again preparing to fulfill their civic duty: filing their state income taxes. The process, while often perceived as daunting, is a necessary element of funding the state's vital services and infrastructure. For the 2024 tax year, which you will file in 2025, the Georgia Department of Revenue (DOR) has established specific guidelines and deadlines that taxpayers must adhere to. Knowing these key dates and requirements is essential for all residents.
The deadline for filing your 2024 Georgia income tax return, or for having it postmarked, is May 1, 2025. This extension from the usual April 15th deadline is a result of hurricane relief efforts. It is important for taxpayers to keep this date in mind to avoid any penalties or complications. While the general rule is April 15th, the Governor can extend the deadline due to unforeseen circumstances.
For those who choose to file their taxes electronically, several advantages make it a favorable option. Electronic filing is often more efficient, providing faster processing and potentially quicker refunds. It also reduces the risk of errors that can sometimes occur with manual filings. The DOR offers resources and guidance on electronic filing, making the process accessible for taxpayers of all levels of familiarity.
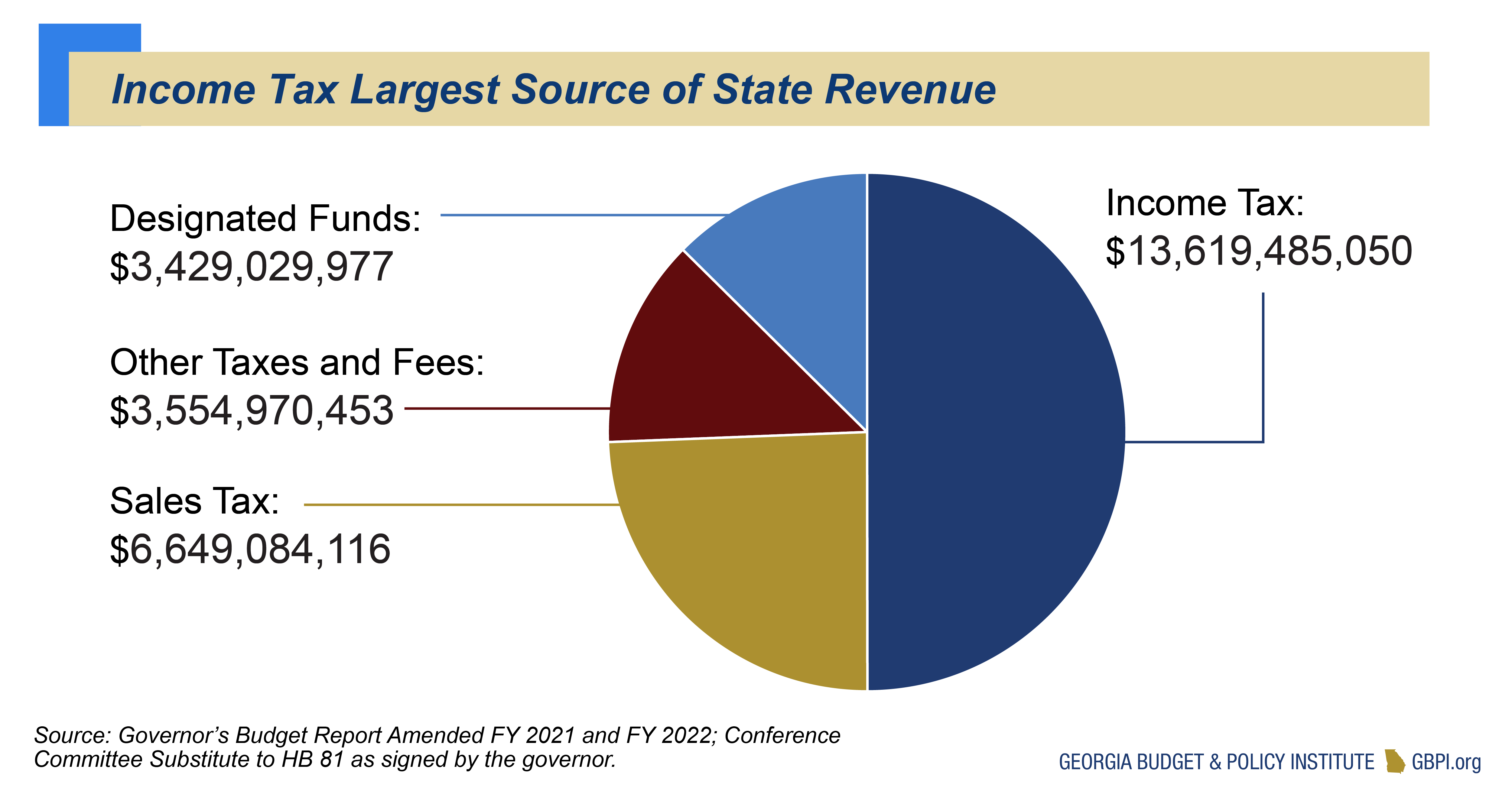
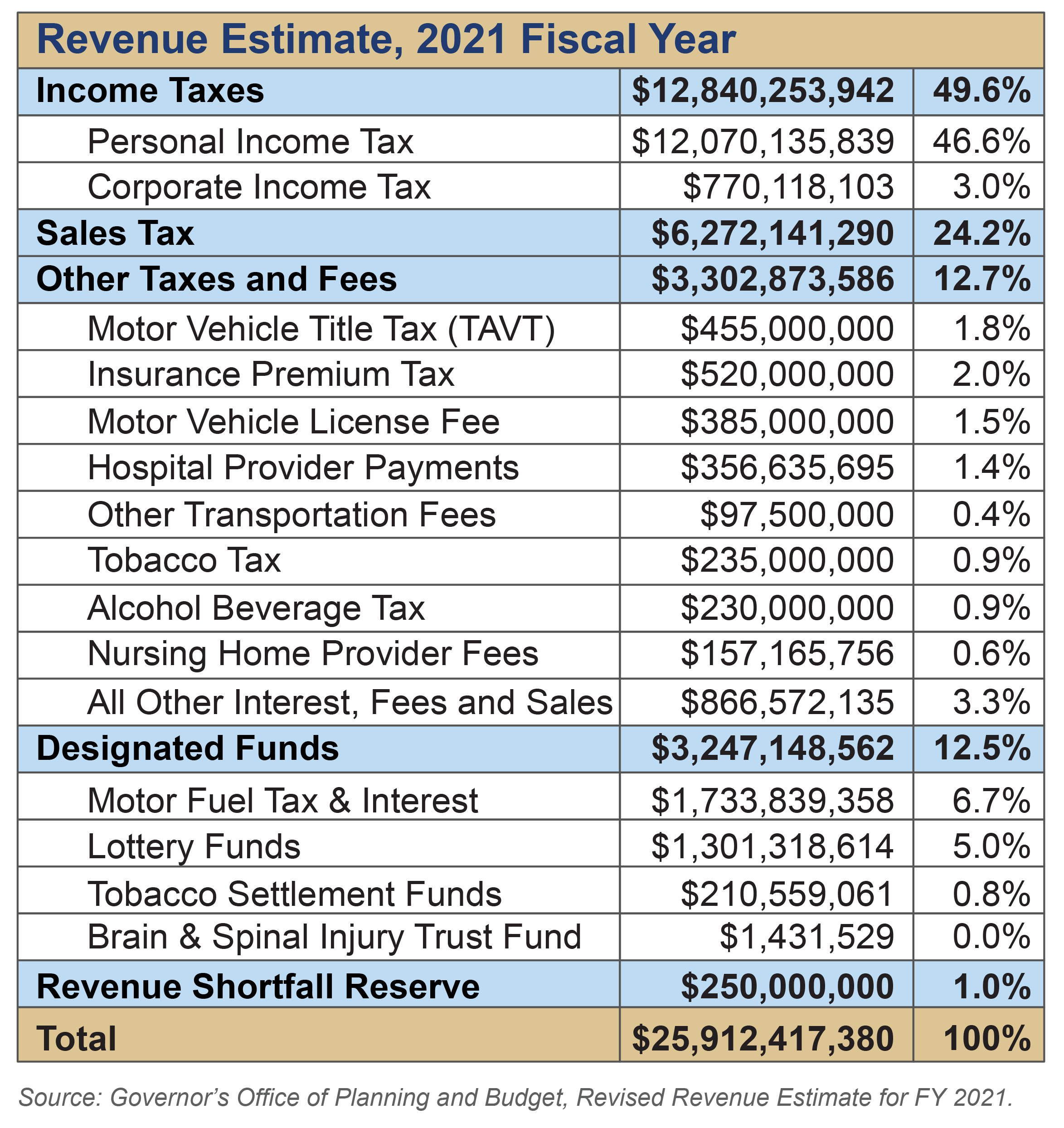
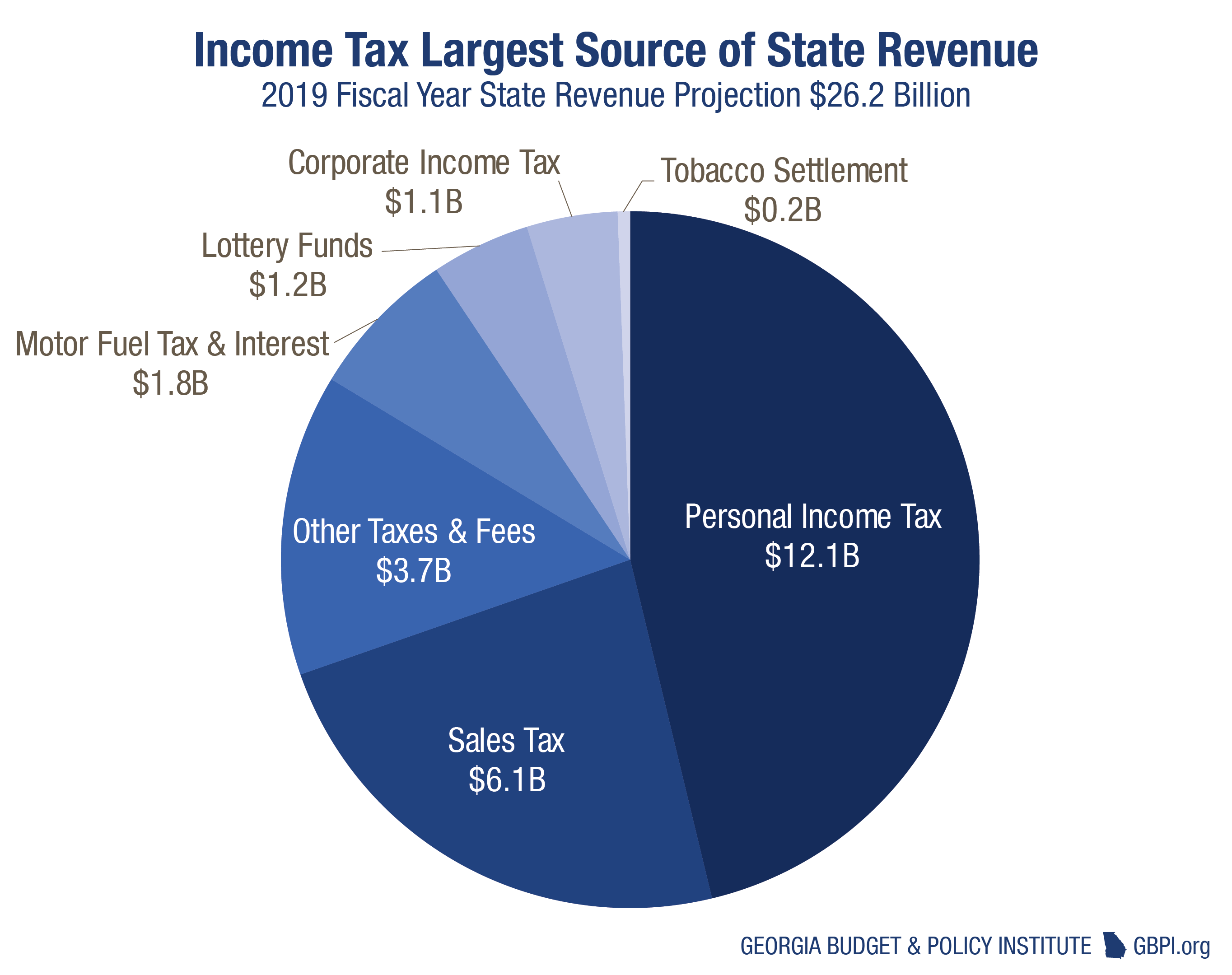
Understanding Georgia's income tax system involves grasping both the tax rate and the factors that influence it. Georgia has adopted a flat state income tax system, which means that all taxable income is subject to the same rate. For the 2024 tax year (filed in 2025), the state income tax rate is set at 5.39%. However, its important to note that this has evolved over time. Beginning in 2024, the rate was set at 5.49%. The Georgia General Assembly passed HB 111, retroactively lowering the state income tax rate from 5.39% to 5.19% on Jan. Looking ahead, the rate will gradually reduce to 4.99% between 2025 and 2029 if economic targets are met.
The Georgia Department of Revenue (DOR) is the principal agency for tax administration and enforcement within the state. They are responsible for administering tax laws, collecting revenue, and providing information and resources to taxpayers. The DOR website serves as a central hub for information, including tax forms, instructions, and updates on changes to tax laws.
A flat tax system ensures every taxpayer pays the same percentage of their taxable income. This is a new system for Peach State residents, who were previously subject to a progressive tax system, which meant higher rates for higher earners. This change brings about a more uniform approach to income tax.
The DOR plays a pivotal role in issuing income tax refunds. The surplus income tax refunds will begin being issued in late May/early June. It is crucial for taxpayers to file both their 2023 and 2024 taxes to be eligible for these refunds.
Many different types of income can be taxed in Georgia. People who earn income in Georgia are required to file state income taxes. Businesses operating in Georgia may need to file taxes on their earnings and may be eligible for various tax credits. Small businesses should familiarize themselves with specific filing requirements to ensure compliance.
Georgia's tax landscape extends beyond income tax. The state also levies taxes on alcoholic beverages, with rates varying based on the type and manufacturing location of the product. For instance, wine is taxed between 11 to 67 cents per liter, while liquor faces a tax of 50 cents to $1.40 per liter. Moreover, local municipalities have the authority to impose additional taxes on groceries, and other local taxes could add up to an additional 4.9%.
Property taxes are another component of Georgia's tax structure. The median property tax in Georgia is approximately $1,346 per year, based on a home valued at $162,800. Counties collect an average of 0.83% of a property's assessed fair market value annually. While the state does not have local income taxes, property taxes contribute to the overall tax burden for homeowners.
Its also important to note that Georgia has among the highest taxes on alcoholic beverages in the country, which is assessed to wholesalers. The peach state charges a $3.79 tax per gallon on distilled spirits and a $0.48 tax per gallon of beer.
The Georgia Tax Center (GTC) is an important online resource for taxpayers. Anyone who pays taxes in the state of Georgia is eligible to use GTC for various services and information. The GTC website allows individuals to manage their tax obligations, access resources, and stay informed about tax-related updates.
In Georgia, distributions and withdrawals from a 401(k) plan are subject to state income tax at the flat rate of 5.19%. However, social security benefits are not subject to state income tax in Georgia. The state excludes this income from state taxes, offering some relief to retirees.
Georgia has established a flat income tax system with a rate of 5.39% applied to all taxable income. This simplifies the tax structure and ensures that all taxpayers pay the same percentage on their income.
Additional Georgia tax changes were effective January 1, 2024. Georgia standard deductions have increased to $24,000 for taxpayers filing married filing jointly. Taxpayers filing single can use this as a base for their personal tax filing.
For businesses, Georgia offers various tax incentives to encourage economic growth. Businesses should apply for these incentives and consider the different programs that support investment, job creation, and economic development. Additionally, identifying approved business tax vendors can help companies navigate the complexities of business taxes.
For the 2024 tax year, the Georgia income tax rate is a flat 5.39%. From 2025 to 2029, the rate will gradually be reduced to 4.99% if certain economic targets are met.
Taxpayers filing single will need to follow the same guidelines as other taxpayers, ensuring that they meet deadlines and accurately report their income.
The Georgia Department of Revenue (DOR) offers a sales tax ID verification tool. Sales tax numbers may be verified using the tool available through the Georgia Tax Center.
Some prescription drugs and medical supplies are exempt from sales tax in Georgia.
Understanding the tax implications on alcoholic beverages and gasoline is crucial. For example, the state charges a tax of 33.05 cents per gallon of gasoline.
When communicating with state entities, verify the authenticity of the website to ensure the security of any sensitive information shared. State of Georgia government websites and email systems use georgia.gov or ga.gov at the end of the address. Before sharing any sensitive or personal information, it is best to make sure you're on an official state website.
Georgia has a population of almost 11 million, and more than half of the population lives in Atlanta. The income tax rate is 5.49% flat. Georgia is ranked number thirty-three out of the fifty states, in order of the average amount of property taxes collected.
As you prepare for tax season, keep these key points in mind. Stay informed, meet the deadlines, and take advantage of the resources provided by the Georgia Department of Revenue. Accurate reporting and timely filing will not only meet your tax obligations but will contribute to a stable and prosperous Georgia.