Is the power of ubiquitous connectivity truly reshaping the world, and if so, how are the tools of the Internet of Things (IoT) leading the charge? The ability to remotely access and manage IoT devices offers a transformative suite of benefits that are revolutionizing industries, enhancing efficiency, and improving the quality of life for individuals across the globe.
The evolution of IoT has been nothing short of remarkable. What began as a niche technology for specialized applications has rapidly expanded into a pervasive network connecting billions of devices. These devices range from the humble smart thermostat in your home to complex industrial machinery operating in remote locations. At the heart of this revolution lies the ability to access and control these devices remotely, unlocking a vast potential for optimization, innovation, and improved operational efficacy. The significance of this remote access cannot be overstated; it is the cornerstone upon which many of the most promising IoT applications are built. This capability empowers users to monitor, manage, and troubleshoot devices from anywhere in the world, offering unprecedented convenience, control, and cost savings.
Consider the implications for businesses. Remote access to IoT devices allows for proactive maintenance, reducing downtime and increasing productivity. Imagine a manufacturing plant where sensors embedded in machinery transmit real-time data on performance, potential malfunctions, and maintenance needs. A technician, located miles away, can access this data remotely, diagnose problems, and even implement solutions without physically being present on-site. This proactive approach not only minimizes disruptions but also extends the lifespan of valuable equipment. Furthermore, remote access facilitates data collection and analysis, enabling businesses to make informed decisions based on real-time insights into their operations. This data-driven approach to management can lead to significant improvements in efficiency, resource allocation, and overall profitability.
The advantages of remote access extend beyond the business realm. In the realm of healthcare, remote patient monitoring systems leverage IoT devices to collect vital signs and other health data, enabling healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely and intervene promptly when necessary. This is particularly crucial for patients with chronic conditions, allowing them to receive personalized care from the comfort of their homes. This not only improves patient outcomes but also reduces the strain on healthcare resources by minimizing hospital visits and freeing up clinicians' time. Similar applications are emerging in the field of agriculture, where sensors and monitoring systems are used to track environmental conditions, soil moisture, and crop health. Farmers can access this data remotely, enabling them to optimize irrigation, fertilization, and pest control practices, leading to higher yields and more sustainable farming practices.
The implications for personal convenience are equally profound. Smart home devices, such as lighting, appliances, and security systems, can be controlled remotely via smartphones or other connected devices. Homeowners can turn on the lights, adjust the thermostat, or lock their doors from anywhere in the world, providing enhanced security, energy efficiency, and peace of mind. This level of control over one's environment has transformed how people interact with their homes, offering a new level of comfort and convenience.
However, the widespread adoption of remote access IoT devices also presents challenges. The most significant concern is security. As more devices become connected to the internet, the risk of cyberattacks increases. Vulnerabilities in device firmware, weak passwords, and inadequate security protocols can expose devices to hacking and data breaches. Therefore, it is essential to prioritize security when designing, deploying, and maintaining remote access IoT systems. This includes implementing robust authentication mechanisms, encrypting data transmission, and regularly updating device firmware to patch security vulnerabilities. Furthermore, educating users about security best practices is crucial to mitigate risks. Users must be aware of the potential threats and take appropriate measures to protect their devices and data.
Another challenge is the complexity of managing a vast network of connected devices. As the number of IoT devices continues to grow, managing and maintaining these devices becomes increasingly complex. This requires specialized expertise and sophisticated tools. Cloud-based platforms are often used to provide a centralized management system for IoT devices, offering features such as device provisioning, monitoring, and remote configuration. However, even with these tools, managing a large-scale IoT deployment can be a significant undertaking. Device interoperability is another major concern. Different IoT devices often use different communication protocols and data formats, making it difficult for them to communicate and share data seamlessly. Standardization efforts are underway to address this issue, but widespread adoption of standardized protocols is still a work in progress. Until interoperability is fully achieved, users may face challenges integrating devices from different vendors into a cohesive system.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of remote access to IoT devices are undeniable. The ability to monitor, manage, and control devices remotely offers unparalleled opportunities for improving efficiency, enhancing security, and improving the quality of life. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of remote access IoT devices, further transforming the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us. The convergence of connectivity, data analytics, and artificial intelligence will likely lead to new and exciting possibilities. For example, advanced analytics can be used to identify patterns and predict potential issues, allowing for proactive maintenance and optimized operations. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence can automate many tasks, such as device configuration, security monitoring, and data analysis. The future of remote access IoT devices is bright, and we can anticipate that they will continue to shape our lives in profound ways.
The advancements in cellular technologies, like 5G, will further bolster the capabilities of remote access IoT devices. With faster speeds and lower latency, 5G networks will enable more reliable and responsive remote control and data transmission, which is especially vital for applications requiring real-time data or immediate responses. This technological leap will enhance the performance of applications across diverse sectors, from smart cities and autonomous vehicles to remote healthcare and industrial automation. Furthermore, the edge computing paradigm will play a crucial role in enhancing remote access capabilities. Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving responsiveness. This is particularly useful for applications where real-time data processing is essential, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation. By processing data at the edge, the reliance on cloud computing is lessened, leading to faster response times and increased reliability. This is especially important in areas with limited or unreliable internet connectivity.
Security, however, remains a paramount consideration. As IoT devices proliferate, the surface area for potential cyberattacks expands. Robust security measures, including end-to-end encryption, secure authentication protocols, and regular security audits, are crucial. It is equally important to create awareness among users about potential threats and the importance of following security best practices. This proactive approach to security will not only protect individual devices but also help to build trust and confidence in the entire ecosystem of connected devices. Additionally, the development of standardized security protocols and guidelines will be necessary for creating a secure and reliable IoT environment.
The evolution of remote access IoT devices is a continuous process, with new innovations emerging constantly. As the technology matures, it will undoubtedly have a more significant impact on our lives and how businesses operate. Addressing the challenges associated with security, interoperability, and complexity will be critical in maximizing the benefits of these devices. With a proactive approach to security, robust management systems, and standardized protocols, remote access IoT devices will continue to enhance efficiency, improve security, and pave the way for a more interconnected and intelligent future.
Key Benefits of Remote Access IoT Devices
The following table highlights some key benefits associated with the adoption of remote access for IoT devices:
| Benefit Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Efficiency | Automation and optimization of processes. Reduced need for on-site intervention. | Remote equipment monitoring, automated inventory management, predictive maintenance. |
| Cost Reduction | Reduced operational costs through preventative maintenance, optimized resource usage, and reduced travel expenses. | Reduced energy consumption, streamlined logistics, and fewer on-site service calls. |
| Enhanced Productivity | Ability to access and control devices from anywhere, enabling faster responses and proactive management. | Remote device configuration, quicker troubleshooting, and improved response times. |
| Increased Security | Real-time monitoring and control of security systems, with immediate response capabilities. | Remote surveillance, intrusion detection, and emergency response. |
| Improved Decision-Making | Data-driven insights for informed decisions based on real-time performance data. | Remote data analysis, predictive analytics, and performance optimization. |
| Enhanced Convenience | Ease of control and management of devices for greater usability. | Remote control of home appliances, smart lighting control, and convenient access to information. |
| Better Accessibility | Offers enhanced accessibility for individuals with disabilities by enabling remote control over assistive technologies. | Remote operation of medical devices, environmental controls, and mobility aids. |
| Sustainability | Optimize resource use through energy management and environmental monitoring. | Smart agriculture, smart grids, and intelligent building management. |
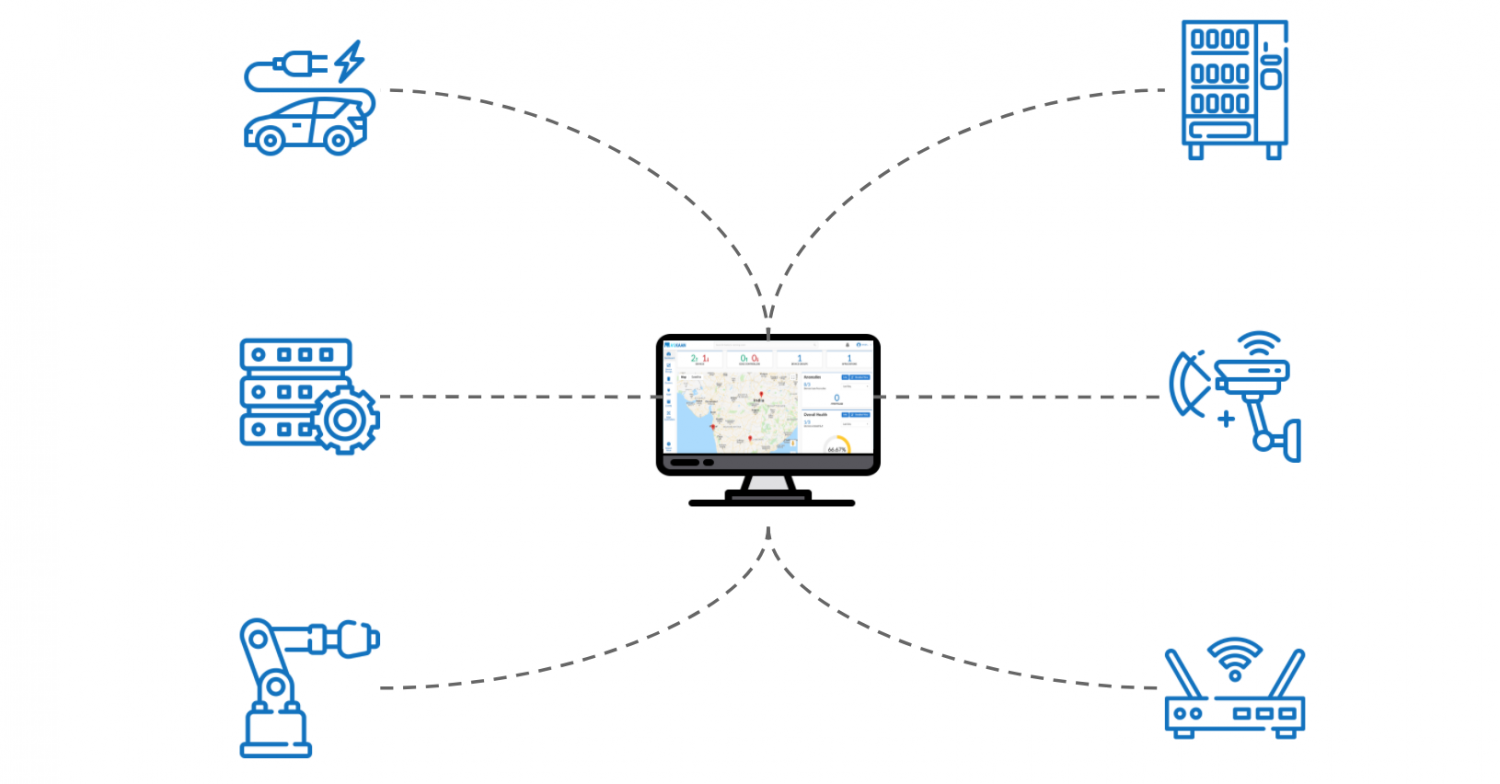
Applications of Remote Access IoT Devices
Below is a table showcasing a range of applications where remote access is transforming industries:
| Application Area | Specific Examples | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Remote monitoring of machinery, predictive maintenance, remote diagnostics. | Reduced downtime, optimized production, improved equipment lifespan. |
| Healthcare | Remote patient monitoring, remote consultations, connected medical devices. | Improved patient outcomes, reduced hospital visits, better access to care. |
| Agriculture | Remote monitoring of soil conditions, automated irrigation systems, precision farming. | Higher yields, reduced resource consumption, optimized crop management. |
| Smart Homes | Remote control of lighting, appliances, and security systems, smart thermostats. | Enhanced convenience, improved energy efficiency, and increased home security. |
| Transportation | Fleet management, remote vehicle diagnostics, connected cars. | Improved efficiency, reduced fuel consumption, and enhanced driver safety. |
| Energy | Smart grids, remote meter reading, and energy optimization. | Reduced energy costs, improved grid stability, and optimized energy distribution. |
| Retail | Inventory management, remote access to point-of-sale systems, and customer experience monitoring. | Improved operational efficiency, data-driven insights, and enhanced customer satisfaction. |
| Environmental Monitoring | Remote monitoring of air and water quality, weather stations, and wildlife tracking. | Improved environmental protection, data collection for scientific research, and enhanced disaster response. |