Are you ready to witness a paradigm shift, a technological revolution redefining how we interact with the world around us? The Internet of Things (IoT), powered by remote task management, is not just a buzzword; it's a transformative force reshaping industries and daily life.
The essence of this transformation lies in the convergence of remote task management and the Internet of Things (IoT). The integration of these two elements has become a game-changer in the rapidly evolving technological landscape, which is essentially redesigning the very fabric of how we manage projects remotely.
To fully appreciate the scope of this innovation, it's helpful to examine the foundational concepts. IoT devices, at their core, are physical objects imbued with sensors and software. These devices are meticulously designed to perform a wide array of remote tasks, enabling automation, data collection, and remote control.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition of IoT | The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical objects ("things") that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the Internet. |
| Key Components |
|
| Applications |
|
| Benefits |
|
| Challenges |
|
| Future Trends |
|
| Reference | IBM - Internet of Things |
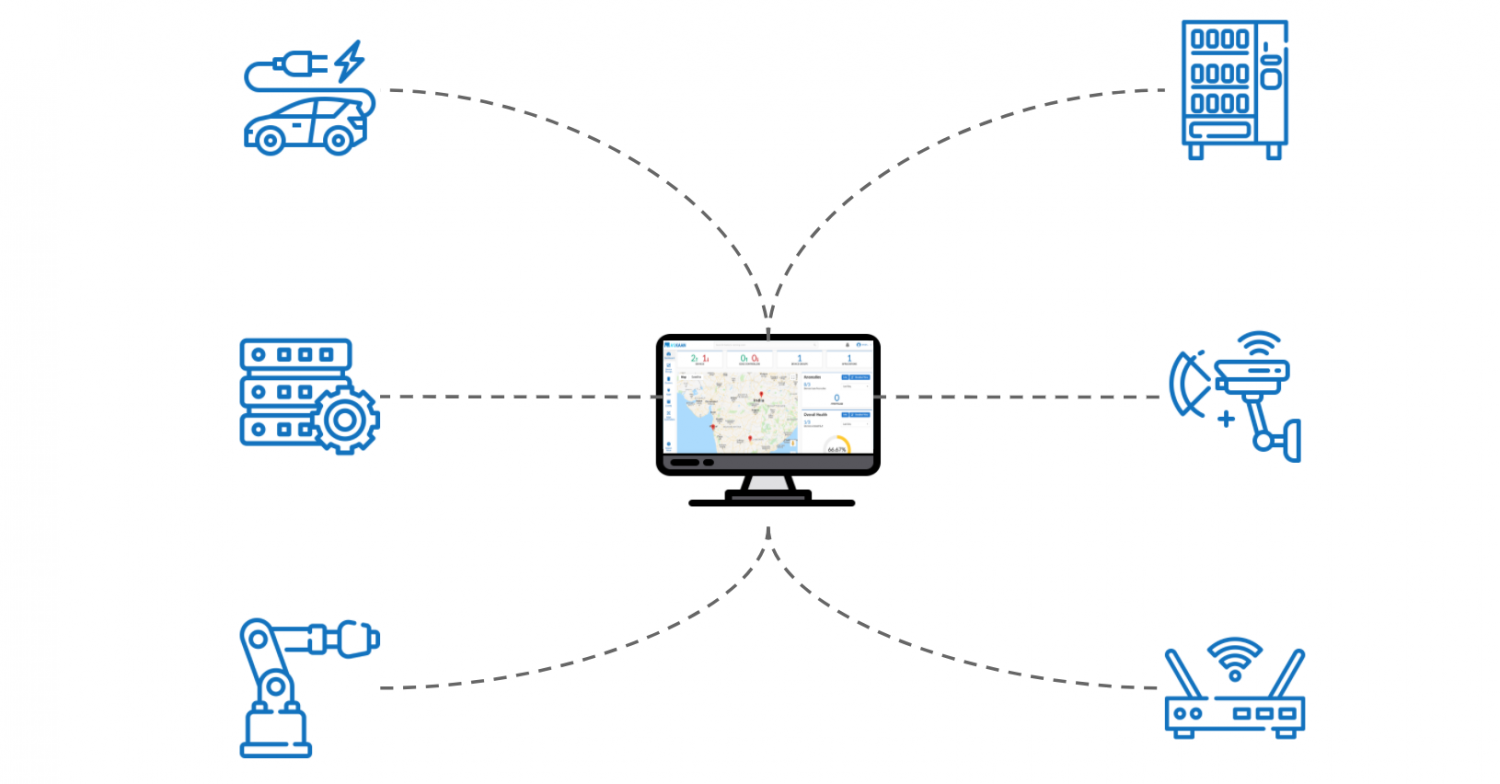
The world of the Internet of Things (IoT) is expanding at an unprecedented rate, and remote IoT device platforms are playing a pivotal role in shaping this digital landscape. As more industries embrace IoT technologies, a clear understanding of remote IoT device platform examples becomes essential for businesses and tech enthusiasts alike.
Consider the myriad applications. From the precision agriculture sector to the complexities of modern healthcare, the versatility and adaptability of remote IoT device management are on full display. These advanced tools and platforms allow organizations to seamlessly monitor and control their IoT devices, ensuring optimal functionality across diverse conditions.
This powerful capability opens doors to countless possibilities across industries, from manufacturing to healthcare. Imagine the implications: Smart sensors and monitors that perform tasks autonomously, made even more effective by the capacity to be remotely accessed and controlled. The main purpose of IoT is to access and operate gadgets from a distance, with little or no human assistance.
Tracking and managing IoT devices is no longer just an operational necessity it is paramount to ensuring the growth and security of any business. The list of IoT applications for businesses is far more comprehensive than the examples mentioned above.
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is a prime example. This system, comprised of interconnected devices within the industrial sector, includes manufacturing machinery and devices used for energy management. IoT devices are found in a wide array of applications, transforming everything from smart cities and cars to smart stethoscopes and dog collars, becoming more commonplace daily. Devices like Nest adjust the temperature based on user preferences and occupancy, saving energy.
Former Google and Alphabet Executive Chairman Eric Schmidt's prediction from a 2015 World Economic Forum panel still rings true: there will be an overwhelming number of IP addresses, devices, sensors, and other connected "things."
The Internet of Things is revolutionizing daily life, enhancing personal convenience in smart homes and improving efficiency in industries like healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, and agriculture.
Take, for instance, the concept of smart home automation, which allows homeowners to monitor and control appliances remotely, enhancing convenience and reducing energy consumption. From lighting to temperature control, these systems streamline daily routines.
IoT also connects devices to exchange data and automate tasks, and remote IoT amplifies this capability, ensuring devices operate effectively regardless of where they are deployed. Maintenance, which involves remote troubleshooting, firmware updates, and hardware diagnostics, is crucial for the smooth functioning of IoT devices.
Remote execute job IoT examples have gained significant traction in recent years, and understanding how to access remote IoT devices is becoming increasingly important.
Each example requires IoT remote management software to facilitate communication between the devices and apps that regulate their activity. Some platforms may excel with specific types of devices. For instance, your system must handle enormous amounts of data if you manage a fleet of sensors.
Consider the innovative IoT device examples of 2025, from smart home gadgets and wearables to industrial sensors. An IoT device management system visualizes collected data and its type based on the remote task within your network.
There are challenges as well. Devices connected to the network become attractive targets for hackers, making IoT device protection one of the most important tasks.
By following this approach, you can implement remote IoT device management, enhancing efficiency and control over business processes. Remote IoT device platforms are transforming how we connect and manage devices in the digital age. Understanding the importance of these platforms, exploring examples, and considering key criteria allows for informed decisions about implementing IoT solutions for your business.
The IoT device management app ensures:
- Simplified device configuration: Remote setup and management of IoT devices.
- Efficient data processing: Real-time data analysis and visualization.
- Improved security: Enhanced device protection and data encryption.
- Proactive maintenance: Predictive maintenance and remote troubleshooting.
- Scalability: Seamless integration of new devices and technologies.
The IoT and advanced technologies are transforming the manufacturing industry and powering a massive digital transformation. From manufacturing automation using robotics and cobotics human/robot collaboration to predicting equipment failure on the factory floor and tracking assets in a warehouse, the industrial IoT is the future of manufacturing.
.jpg)