Is the Californian sun truly as predictable as we believe? Sacramento's average temperature, a seemingly simple statistic, holds a wealth of information, reflecting not just the city's climate but also its relationship with the environment and the subtle shifts occurring year after year.
Sacramento, the capital city of California, enjoys a Mediterranean climate, characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. This climate is heavily influenced by its location in the Central Valley, a vast agricultural region cradled between the Sierra Nevada mountains to the east and the Coast Range to the west. But what precisely constitutes the "average temperature" in this sun-drenched city? It's a question that unlocks a deeper understanding of Sacramento's weather patterns and their potential future trajectories. The term "average temperature" is a calculated value, determined by taking the sum of all temperature measurements over a specific period typically a month, a season, or an entire year and dividing by the number of measurements. This gives us a single number that represents the typical thermal experience of a place. The calculation itself sounds simple, but the implications are profound. It allows us to compare temperatures across different time periods and identify trends. It provides a baseline for understanding extremes. And, perhaps most importantly, it offers a window into the effects of climate change.
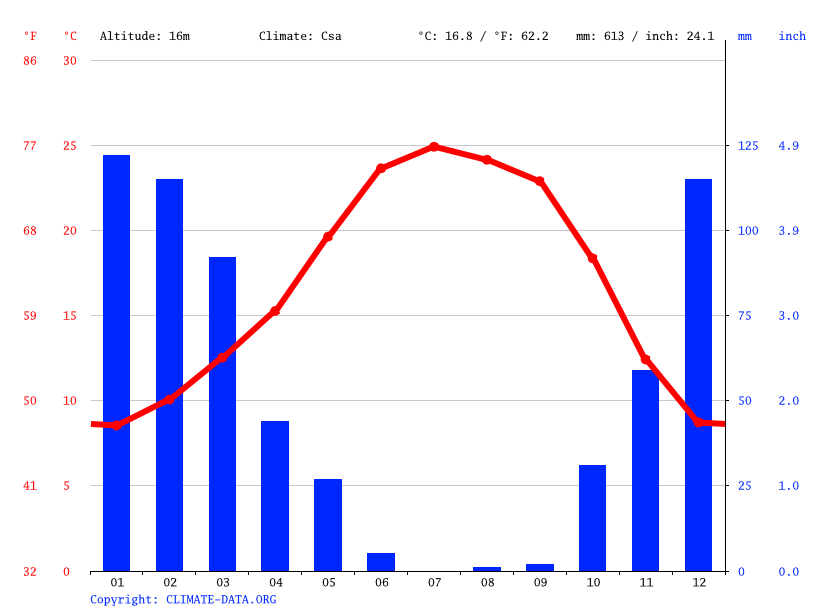
The specific figures for Sacramentos average temperature fluctuate depending on the season and the time frame considered. Generally, summer months, particularly July and August, see the highest average temperatures, often hovering around the low to mid-90s Fahrenheit (32-35 degrees Celsius) during the day. Nights are typically cooler, providing some respite from the daytime heat. Winter months, such as December and January, bring the lowest average temperatures, with daytime highs in the low to mid-50s Fahrenheit (10-13 degrees Celsius) and nighttime lows often dipping into the 30s (0-4 degrees Celsius). The shoulder seasons, spring and autumn, offer a more moderate climate, with temperatures gradually transitioning between the extremes. It is crucial to understand that these are averages. Daily temperatures can vary significantly. A heatwave can push temperatures well above the average, while a cold snap can bring unexpected chills. These variations are part of the natural rhythm of weather, but they can also be influenced by larger climate patterns.
The data used to calculate Sacramento's average temperature is meticulously collected and maintained by meteorological agencies, such as the National Weather Service (NWS). These agencies operate weather stations throughout the city, equipped with sensors that constantly monitor temperature, humidity, wind speed, precipitation, and other atmospheric variables. The data collected is then processed and analyzed to provide valuable insights into the city's climate. The accuracy and reliability of this data are critical, as they form the foundation for understanding climate trends, forecasting weather, and informing decisions related to public health, infrastructure, and resource management. The methodologies employed are standardized to ensure consistency and comparability of data across different locations and time periods. This detailed record-keeping enables scientists and researchers to look at changes over time, and recognize any shifts that might suggest larger climate alterations.
The impact of Sacramento's average temperature extends far beyond the simple experience of comfort or discomfort. It influences nearly every facet of life in the city. Agriculture, a cornerstone of the Central Valley's economy, is directly affected by temperature fluctuations. Crop yields, planting schedules, and irrigation requirements are all determined by the thermal characteristics of the region. The city's infrastructure, from its roads and bridges to its power grids and water systems, is also designed to withstand specific temperature ranges. Extreme heat can strain these systems, leading to power outages, road damage, and water shortages. Public health is significantly impacted. High temperatures can exacerbate heat-related illnesses, such as heatstroke and dehydration, particularly among vulnerable populations like the elderly and the young. The average temperature also affects the types of activities that people engage in, influencing tourism, outdoor recreation, and even social gatherings. Sacramentos river and waterways, the lifeblood of the city, see their flow and ecosystem affected by the average temperature influencing the levels of snowmelt from the Sierra Nevada mountains, and the evaporation rates of the water in the city itself.
One of the most pressing concerns surrounding Sacramento's average temperature is the influence of climate change. There is a growing body of evidence indicating that average temperatures in the city are rising, and that this trend is likely to continue. This is not just a matter of warmer summers. It also involves changes in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as heatwaves and droughts. Climate models predict that Sacramento will experience more frequent and prolonged periods of extreme heat, leading to increased health risks and infrastructural challenges. Changes in precipitation patterns are also anticipated, with the potential for longer dry seasons and more intense rainfall events. These changes pose a significant threat to Sacramento's economy, environment, and quality of life. The city is responding to this challenge through various initiatives, including promoting energy efficiency, investing in renewable energy sources, and developing adaptation strategies to mitigate the effects of climate change.
Understanding Sacramento's average temperature and its trends is essential for making informed decisions about the future. It requires continuous monitoring of climate data, a commitment to scientific research, and collaboration between government agencies, businesses, and the community. This data helps us better understand how climate change impacts the city and the steps we can take to adapt. It can guide urban planning and infrastructure development, influencing how new housing and commercial construction is designed to respond to more frequent high-temperature events. Also, it can ensure that emergency preparedness protocols are well equipped to respond to sudden heatwaves or drought conditions. Furthermore, a deep understanding of average temperature informs the decisions of local agriculturalists, who need to prepare for altered growing seasons and the potential for decreased yields. Sacramento's story, a microcosm of the larger global narrative, highlights the need for proactive, science-based solutions to climate change. This involves individual responsibility, governmental support, and a unified effort to address what may be the defining challenge of our time.
Here's a breakdown of some key temperature averages, to provide a more in-depth perspective on Sacramento's climate:
| Month | Average High Temperature (F) | Average Low Temperature (F) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 54 | 39 | Typically the coolest month. |
| February | 59 | 42 | Transitioning out of winter. |
| March | 64 | 45 | Spring begins to take hold. |
| April | 71 | 48 | Temperatures steadily increase. |
| May | 80 | 54 | Warm days become more common. |
| June | 88 | 59 | Summer approaches with increasing heat. |
| July | 94 | 63 | Hottest month, on average. |
| August | 93 | 62 | Similar to July, with high temperatures. |
| September | 89 | 59 | Slight cooling trend begins. |
| October | 79 | 51 | Pleasant autumn weather. |
| November | 63 | 43 | Temperatures decline further. |
| December | 55 | 39 | Winter settles in. |
The historical records of Sacramento's average temperature reveal an intriguing, though sometimes sobering, story. These records, often stretching back over a century, document the subtle, yet significant, shifts in climate patterns. They show the fluctuations and the long-term trends that underscore the impact of climate change. When examining these records, climate scientists and meteorologists utilize sophisticated tools to analyze the data and extract meaningful insights. They account for a number of factors that can influence the accuracy of measurements, such as changes in the location of weather stations, or the use of different measuring equipment. The long-term trend is clear: Sacramento is, on average, experiencing warmer temperatures than it did in the past. The incremental increases, even if seemingly small year by year, accumulate over time and lead to significantly warmer conditions. For example, a recent study found that Sacramento's average annual temperature has risen by several degrees Fahrenheit over the past century. This trend is consistent with global patterns of warming, and it underscores the urgent need to address climate change. It is crucial to understand that climate change does not involve simply increasing the average temperature. It involves an alteration of the entire climate system.
The concept of the "normal" temperature, used by meteorologists, provides a useful reference point for understanding how the weather is changing. Normal temperatures are derived by averaging the temperature over a 30-year period, which means this "normal" is constantly evolving as we gather more data and the climate changes. The idea of these averages is to smooth out the day-to-day fluctuations and identify long-term patterns. By comparing current temperatures to the normal, we can determine whether a given month, season, or year is warmer or colder than average. These comparisons help us understand climate variability and recognize the emergence of climate change. The "normal" serves as a valuable tool for interpreting and communicating climate information to the public. Also, understanding the normal allows us to make informed decisions about the present. Knowing the normal high temperature for a July day in Sacramento allows the citys health officials to prepare for expected peaks in heat-related illnesses. However, a consistently rising normal is itself an indication of the overall rise in temperature.
The concept of "microclimates" also plays a significant role in understanding Sacramentos average temperature. Microclimates are localized climate conditions that can differ significantly from the broader regional climate. Within Sacramento, factors such as proximity to the Sacramento River, the presence of urban heat islands, and the density of vegetation can all influence the temperature. The Sacramento River, for example, can provide a cooling effect during the hot summer months. Urban heat islands, caused by the concentration of buildings, roads, and other infrastructure, tend to trap heat and raise temperatures in urban areas. Conversely, green spaces, such as parks and tree-lined streets, can help to mitigate the heat and provide a cooler environment. This variation underlines the importance of understanding the temperature not just as a citywide average but as a complex tapestry of localized conditions. To fully understand the thermal environment of the city, it's necessary to consider the microclimatic differences. The variability within the city, whether it is the cooling effect of the river, or the heating effects of the built-up urban areas, can impact the individual experience of average temperature.
The future of Sacramento's average temperature is intertwined with global climate change. As greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise, the Earth's climate is warming, and the effects are already visible in Sacramento. Climate models predict that the city will experience further increases in average temperatures, with more frequent and intense heatwaves, and less predictable precipitation patterns. These changes will impact various aspects of life in the city. The citys water resources, already stressed by drought, are expected to become scarcer. The risks to public health will increase, as heat-related illnesses become more common. Agricultural production will face new challenges, as crop yields are affected by changing climate patterns. The city is committed to proactive measures to address climate change. These include a focus on renewable energy, energy-efficient building standards, and a commitment to enhancing the citys resilience to extreme weather events. Addressing climate change will require the cooperation of government at the local, state, and national levels. It will also need the involvement of businesses, community organizations, and individuals. The city is committed to pursuing these measures, because this will be crucial to the overall health of Sacramento and its environment.
The impact of Sacramento's average temperature extends beyond the realm of physical comfort and infrastructural concerns. It also has cultural and social ramifications. The city's outdoor lifestyle, its vibrant arts scene, and its diverse community are all influenced by the climate. The hot summers, for example, have historically shaped Sacramento's cultural identity, with residents adapting to the heat through leisurely activities and a distinctive sense of community. Sacramento's commitment to urban forestry, with its tree-lined streets and verdant parks, reflects a cultural appreciation for the role of green spaces in mitigating the heat and improving the overall quality of life. These green spaces create a social environment that is welcoming and encourages outdoor activities. As the average temperature changes, these cultural and social aspects of life in Sacramento will also be impacted. The city will need to adapt its cultural landscape to accommodate changes in climate, and it will need to find new ways to maintain its vibrant social life.
In conclusion, the concept of Sacramento's average temperature is much more than just a number. It is a key measure of the environment. It provides us with valuable insight into the city's weather patterns, the influence of climate change, and the overall dynamics of its ecosystem. The understanding of this number is crucial for the residents of Sacramento. This understanding helps them to adapt to a changing climate and protect the future of their city. As the climate continues to evolve, a commitment to scientific research, data collection, and collaborative action will be essential for ensuring the long-term health and sustainability of Sacramento and its people. The focus on the average temperature highlights the need for proactive solutions to climate change, and for the development of new methods of sustainability. The average temperature will continue to tell the story of Sacramento and the world.