Are you tired of your cloud computing costs spiraling out of control? Understanding and optimizing your Amazon Web Services (AWS) NAT Gateway expenses is a critical step in managing your cloud infrastructure budget effectively.
Navigating the complexities of cloud computing often involves making critical decisions about resource allocation and cost management. One area that frequently presents both challenges and opportunities for optimization is the use of Network Address Translation (NAT) Gateways. These gateways facilitate outbound internet access for your private instances within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), but they come with associated costs that can quickly add up if not managed efficiently. This article delves into the intricacies of AWS NAT Gateway pricing, offering insights and strategies to help you minimize your data transfer charges and overall expenses.
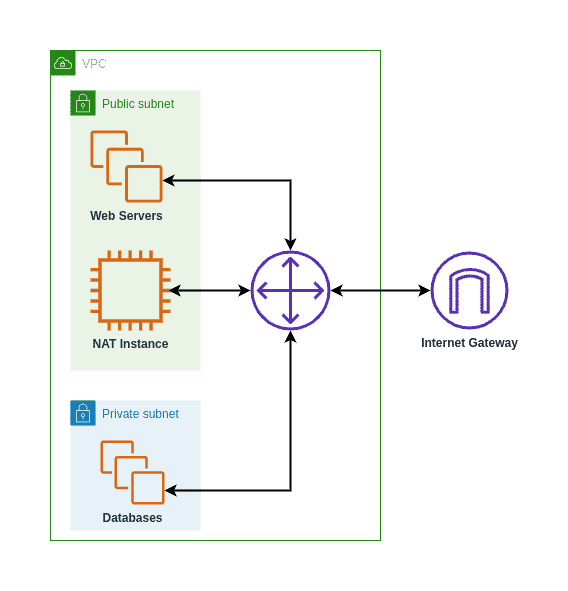
Before we dive into optimization strategies, let's establish a clear understanding of what a NAT Gateway is and how AWS charges for its use. A NAT Gateway acts as a translator, allowing instances within your private subnets to initiate connections to the internet or other AWS services without exposing their private IP addresses. This provides a crucial layer of security and control, enabling you to regulate network access and data flow. However, this functionality comes at a cost.
AWS NAT Gateway pricing is primarily based on three factors:
- Hourly Charge: A fixed fee for each hour the NAT Gateway is provisioned and available.
- Data Processing Charge: A fee based on the amount of data processed by the NAT Gateway, applied per gigabyte (GB).
- Data Transfer Charge: Standard data transfer charges apply for data moving between your instances and the internet, as well as between different AWS Availability Zones.
Let's assume you've created a NAT Gateway and an EC2 instance is routing to the internet through it. From there, the costs start accruing from hourly charges to data processing to data transfer. The data transfer cost is also a major factor, as the rate can be different based on the destination of the data. This cost can easily rise if proper optimization isn't done at the beginning.
Now, lets look at the specifics of AWS NAT Gateway and how to make sure that the expenses dont become a burden to your budget.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | A managed Network Address Translation (NAT) service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) for enabling outbound internet access from private subnets within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). |
| Purpose | Allows instances in private subnets to connect to the internet, other AWS services, or on-premises networks without requiring public IP addresses, enhancing security. |
| Key Features |
|
| Pricing Model |
|
| Cost Optimization Strategies |
|
| NAT Gateway vs. Internet Gateway |
|
| NAT Gateway vs. NAT Instance |
|
| Security and Compliance | Can be used to meet various security and compliance requirements by controlling network access and data flow. |
| Use Cases |
|
| Example Cost Calculation |
|
For a more detailed and accurate understanding of AWS NAT Gateway, you can refer to the official AWS documentation: https://aws.amazon.com/vpc/nat-gateway/
When you provision a NAT Gateway, you're essentially paying for two primary components: the hourly charge and the data processing charge. The hourly charge is a fixed cost, based on the time the gateway is active. The data processing charge, on the other hand, is variable and depends on the amount of data your NAT Gateway handles. This means that the more data your instances transfer through the gateway, the higher the data processing costs will be.
Considering the variable nature of data processing costs, its easy to see how your NAT Gateway expenses can fluctuate. This is why actively monitoring and optimizing data transfer is crucial. Use the AWS Pricing Calculator to model different scenarios and forecast your costs.
So, how can you optimize your AWS NAT Gateway costs? Here are five key steps to help you:
- Choose the Right NAT Device: Consider the alternatives. While NAT Gateways offer ease of management, NAT instances (EC2 instances configured for NAT) might be a cost-effective choice for specific use cases. However, NAT instances require more manual management and are less scalable than NAT Gateways. Select the option that best fits your needs, considering factors like bandwidth requirements, availability needs, and your teams operational capabilities.
- Use Interface Endpoints or Gateway Endpoints: Take advantage of VPC endpoints. For traffic to other AWS services such as S3 or DynamoDB, consider using VPC interface endpoints or gateway endpoints. These endpoints allow your private instances to access these services without going through the NAT Gateway, bypassing the data processing charges altogether. This can lead to significant savings, particularly if your applications heavily utilize these AWS services.
- Optimize Data Transfer: Evaluate your data transfer patterns. Are your instances transferring large volumes of data? Look for opportunities to reduce data transfer volume. This can include optimizing your code to send only the necessary data or compressing data before transfer. In addition, ensure that your resources and the NAT Gateway are located within the same Availability Zone (AZ) to avoid inter-AZ data transfer charges.
- Monitor Data Usage: Implement robust monitoring. Regularly monitor your NAT Gateways data processing volume and data transfer costs using AWS CloudWatch. Set up alerts to notify you of any unexpected spikes in usage, which could indicate a problem or an opportunity for optimization.
- Right-Size Your NAT Gateway: Ensure proper sizing. A single NAT Gateway can often meet the needs of an entire VPC, scaling automatically to handle traffic. Avoid over-provisioning.
Lets consider a scenario to further understand the practical implications of cost optimization. Suppose you have an EC2 instance in a private subnet that needs to access an API hosted on the internet. The instance routes its traffic through a NAT Gateway. You also have several Lambda functions in the same VPC that need to access a database and third-party APIs.
Initially, all outbound traffic from both the EC2 instance and the Lambda functions goes through the NAT Gateway. The NAT Gateway is charged for both hourly usage and data processing. The data transfer charges also apply as the instance is sending the data.
However, by implementing the following optimizations, you can reduce costs:
- Utilize VPC Endpoints: For the Lambda functions' access to the database (if its an AWS service like RDS), use VPC interface endpoints. This allows the functions to connect directly to the database without going through the NAT Gateway, eliminating the data processing charges for that traffic.
- Optimize Data Transfer: For the EC2 instance's API calls, evaluate the data being transferred. Can the data be compressed to reduce the volume? Are there API calls that can be optimized or eliminated?
- Monitor and Adjust: Continuously monitor the NAT Gateways CloudWatch metrics. Track data processing and data transfer costs. If the API traffic from the EC2 instance remains high, explore alternative architectures, such as using a proxy server within the VPC.
In this scenario, by strategically using VPC endpoints and optimizing data transfer, you can significantly reduce your data processing costs and overall expenses associated with the NAT Gateway.
Another important aspect to consider is the difference between a NAT Gateway and an Internet Gateway. An Internet Gateway allows instances with public IP addresses to directly access the internet. This is suitable for instances that require direct inbound connectivity. In contrast, a NAT Gateway provides outbound internet access for instances in private subnets, without assigning them public IP addresses. The choice between these depends on your specific security and connectivity requirements.
The AWS Pricing Calculator is an invaluable tool for estimating and planning your NAT Gateway costs. It allows you to model different scenarios based on your anticipated data transfer volume and the duration of NAT Gateway usage. By using the calculator, you can gain a clear understanding of the potential costs and make informed decisions about your infrastructure design.
When creating your resources, it's crucial to ensure they are in the same Availability Zone (AZ) as the NAT Gateway. This minimizes data transfer costs. Inter-AZ data transfer is more expensive than data transfer within the same AZ. If your resources are spread across multiple AZs, consider deploying a NAT Gateway in each AZ to reduce costs and maintain high availability.
The cost of a NAT Gateway is impacted by the AWS region you choose. The price varies by region. This is why it is important to select the appropriate region that is also closest to your users to reduce latency. Be sure to check the AWS pricing page for the most current pricing information for each region.
One frequently asked question is whether you receive multiple NAT Gateways when setting up a VPC with a standard configuration. By default, when you create a NAT Gateway, you get one. However, you can create multiple NAT Gateways, especially if you need high availability and redundancy across multiple Availability Zones. Each NAT Gateway is independent, and the cost is multiplied based on the number of gateways you are running.
Another important consideration is the relationship between your data processing and data transfer costs. Data processing charges are for the data that the NAT Gateway processes, while data transfer charges apply when moving data between different AWS services or the internet. Optimizing both is essential. For instance, if 1 GB of data is transferred from an EC2 instance through a NAT Gateway to S3 within the same region, you may not incur data transfer charges because the data transfer is within the same region. However, the NAT Gateway will still incur data processing charges for that 1 GB.
While Amazon EC2 reserved instances or spot pricing are not available for NAT Gateways, there are still ways to optimize costs. By choosing the right NAT device, implementing VPC endpoints, optimizing data transfer, monitoring data usage, and properly sizing your NAT Gateway, you can minimize your costs and ensure that your cloud infrastructure remains cost-effective.
In conclusion, managing NAT Gateway costs is an essential part of effective cloud financial management. By understanding the pricing components, implementing optimization strategies, and continuously monitoring your usage, you can significantly reduce your expenses and ensure a cost-efficient cloud infrastructure. Remember to always review AWS pricing, use the AWS Pricing Calculator, and stay informed about the latest best practices to optimize your cloud spending.